- The Law of Action-Reaction (Revisited)
- Momentum Conservation Principle
- Isolated Systems
- Using Equations as a Recipe for Algebraic Problem-Solving
- Using Equations as a Guide to Thinking
- Momentum Conservation in Explosions
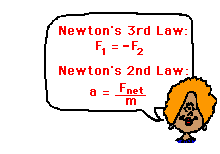
A collision is an interaction between two objects that have made contact (usually) with each other. As in any interaction, a collision results in a force being applied to the two colliding objects. Newton’s laws of motion govern such collisions. In the second unit of The Physics Classroom, Newton’s third law of motion was introduced and discussed. It was said that…
… in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects. The size of the force on the first object equals
the size of the force on the second object. The direction of the force on the first object is opposite
to the direction of the force on the second object. Forces always
come in pairs – equal and opposite action-reaction force pairs.
